Leonardo Tang
Welcome! I'm a Research Specialist at Emory University Department of Radiology and Imaging Science under Dr. Hui Mao specializing in deep learning architectures for medical imaging data. My work focuses on adapting state-of-the-art computer vision techniques to solve complex real world problems in medical imaging. Ongoing research includes leveraging feature modulation and custom loss functions with frequency priors to enhance diffusion probabilistic models for MR spectroscopy denoising, as well as designing robust pipelines for multi-modal prostate cancer analysis. I am seeking a PhD to research balancing emergence abilities with domain-specific priors; specifically, I aim to explore how explicit inductive biases can be introduced to guide models toward physically adherent latent representations. Feel free to email me if you have any research questions!
Email / Google Scholar / CV
Publications

Glymphatic dysfunction in pediatric-onset multiple sclerosis and anti-myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein antibody associated disorder [Scientific Poster]
8th Annual American Society of Pediatric Neurology Scientific Meeting (ASPNR 2026, Upcoming)
soon
Anti-myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG) associated disorder (MOGAD) is a neuroinflammatory disease that can mimic other demyelinating diseases, such as multiple sclerosis (MS). Dysfunction of the glymphatic system, a lymph-like system for the brain, may contribute to neuroinflammation. Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) along the perivascular space (DTI-ALPS) can be used to evaluate glymphatic dysfunction. and has been used to assess glymphatic dysfunction in adults with MOGAD and in pediatric MS, but not in pediatric MOGAD. Here we measure glymphatic dysfunction using DTI-ALPS in children with MS and MOGAD. A prospective, cross-sectional study was conducted involving pediatric patients diagnosed with pediatric-onset MS (POMS) or MOGAD, as well as control patients obtaining brain imaging without a diagnosed neurologic disorder

Impairments in functional connectivity and glymphatic system in breast cancer patients undergoing treatment [Digital Poster]
2025 International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine Annual Meeting & Exhibition (ISMRM)
abstract
Altered DMN-based functional connectivity and bilateral ALPS-index, as well as the negative correlation between elevated posterior cingulate cortex-precuneus connectivity and ALPS-index in BC, indicate a potential mechanism overcoming glymphatic dysfunction by enhancing functional interactions.

Investigating prognostic value of dynamic susceptibility contrast perfusion MRI-derived features for glioblastoma survival by deep learning [Digital Poster]
2025 International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine Annual Meeting & Exhibition (ISMRM)
abstract
Using our Hierarchical Density-Based Network (HDBNet) to investigate hemodynamic information in dynamic susceptibility contrast perfusion-weighted imaging (DSC-PWI) reveals key features that can enhance GBM prognosis, supporting the importance of including hemodynamic and physiological imaging data in future GBM research.

Altered cerebrospinal fluid dynamics in Alzheimer's disease as measured by resting-state fMRI [Digital Poster]
2025 International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine Annual Meeting & Exhibition (ISMRM)
abstract
Investigating rsFMRI data revealed distinct patterns in CSF flow dynamics among AD and MCI subjects compared to normal controls, providing a foundation to improve the characterizations of AD or other degenerative diseases.

Revealing hemodynamic heterogeneity in glioblastoma and medulloblastoma by deep-analysis of dynamic susceptibility contrast-enhanced MRI data [Oral Presentation]
2024 Radiological Society of North America Annual Meeting (RSNA)
abstract
Wholistically analyzing time course profiles from DSC MRI can improve the segmentation of the tumors while revealing the intertumoral hemodynamic heterogeneity of tumors and TME in GBM and MB. We demonstrated that proposed neural network is capable of delineating tumor tissue subtypes within the TME and extracts relevant time course signal features. MB exhibits fewer hemodynamically distinctive tumor tissue subtypes, suggesting a lower degree of intratumoral heterogeneity compared to GBM.
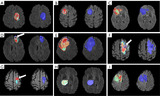
Hemodynamic property incorporated brain tumor segmentation by deep learning and density-based analysis of dynamic susceptibility contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
Quantitative Imaging in Medicine and Surgery, 2024
bib / paper
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a primary non-invasive imaging modality for tumor segmentation, leveraging its exceptional soft tissue contrast and high resolution. Current segmentation methods typically focus on structural MRI, such as T1-weighted post-contrast-enhanced or fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) sequences. However, these methods overlook the blood perfusion and hemodynamic properties of tumors, readily derived from dynamic susceptibility contrast (DSC) enhanced MRI. This study introduces a novel hybrid method combining density-based analysis of hemodynamic properties in time-dependent perfusion imaging with deep learning spatial segmentation techniques to enhance tumor segmentation.

Improving glioblastoma segmentation with deep learning and hemodynamic Information from dynamic susceptibility contrast-enhanced MRI [Poster Session]
2023 World Molecular Imaging Conference (WMIC)
abstract
By utilizing a density-based machine learning approach to analyze the time course profiles resulting from voxels within a region of interest (ROI) specified by a deep neural network used for tumor segmentation, we can use the information captured by 4D DSC data to further improve tumor segmentation. When evaluating precision of mask generation, calculated as the true positive (tp) divided by the sum of the tp and the false positive (fp), we find that U-Net alone outputs a 92.63% score while the full algorithm yields 94.57% score, indicating that the algorithm increases the overall precision of the segmentation.
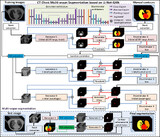
Automatic multiorgan segmentation in thorax CT images using U-net-GAN
Medical Physics, 2019
bib / paper
We have investigated a novel deep learning-based approach with a GAN strategy to segment multiple OARs in the thorax using chest CT images and demonstrated its feasibility and reliability. This is a potentially valuable method for improving the efficiency of chest radiotherapy treatment planning.